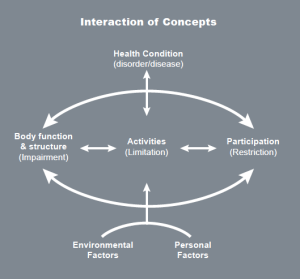
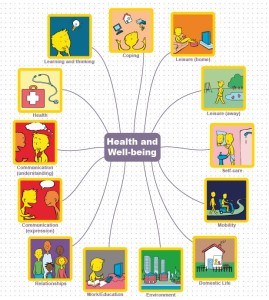
The Health and Well-being resource is based on the WHO International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) which is a framework which covers almost every aspect of daily life and can be applied over different cultures (WHO 2001).
Use of the WHO ICF helps professionals to think holistically about the people they are working with. We have produced four sets of symbols, based on WHO ICF, to help people express their views about different aspects of their lives. These cover 13 topics:
You can use the symbols in different ways, depending on the cognitive abilities of the person you are working with. For example, if you are working with someone who can understand abstract concepts, you could start with the 13 main health and well-being symbols. Your top scale might be ‘managing’ and ‘not managing’. Here is an example of a mat completed by Duncan who had a stroke which affected his ability to communicate through speech:
Using these symbols as a starting point, Duncan could tell us that his main concerns related to worries about his health, expressive communication and work. From here, we did ‘sub mats’ to help Duncan identify the specific areas he wanted to work on/explore.
Here is the mat Duncan completed in relation to his health:
Having done this mat with Duncan, it became clear that he was worried about various aspects of his health, particularly the risk of having another stroke. The wider team were able to give him and his wife information about stroke prevention. Other mats were also completed, exploring expressive communication, work and education and higher level communication (which is included in the ‘learning and thinking’ topic, and covers written communication as well as memory and concentration). Using the Health and Well-being symbols, we were able to work with Duncan to help him identify the main issues that he wanted to work on and then work towards more specific rehabilitation goals. Duncan had copies of all the mats he had completed and found it useful to refer to them over the months. This helped everybody stay on track in relation to his goals and he was also able to track his progress over time.
Have a look at our Health and Well-being resource on our website. It is available both as an original Talking Mat with a physical mat and symbol cards or as a digital version as part of The Talking Mats pro subscription
I like my iPad and I LOVE the new Talking Mats app.
My 89 year old mum lives on her own about 2 hours from where I live and enjoys looking at photos on my iPad Mum has ‘all her marbles’, as the saying goes, and freely expresses her extreme views on current affairs, politics and photographs in Hello magazine! More difficult however, is discussing her failing energy levels and physical strength. She has till now resisted all suggestions of moving house to somewhere with more support.
I knew she would be interested in the Talking Mats app and a demonstration one afternoon flowed naturally into the Domestic topic of the Health and Well Being section. Suddenly we were in the middle of that difficult conversation we’d both been avoiding. Mum fully engaged with the app and changed the position of some items after consideration
The reality is she isn’t managing, she’s struggling. For the first time using the Talking Mats app she confessed to all domestic tasks being difficult even with the bits and pieces of help going in regularly.
The app made that bit easy. Making a decision about the next step will be more difficult.
Rhona Matthews
For those of us who work or live with people with communication difficulties it’s important that we consider the purposes of human communication. As long ago as 1988 Janice Light suggested that there were 4 main purposes and we believe this is still a good model to bear in mind.
(Light, J. (1988) “Interaction involving individuals using augmentative and alternative communication systems: state of the art and future directions”, AAC, 4, 2, 66-82)
She described these purposes as:
1. Expression of needs and want – to regulate the behaviour of another person to get something
2. Information transfer – to convey information from person A to person B
3. Social closeness – to establish and maintain relationships with others
4. Social etiquette – to conform to the social conventions of politeness
We believe that there is a tendency to concentrate too much on 1 and 2 and not enough on 3 and 4. If we dwell on needs and wants, which is very often the focus of communication aids, there is a danger that the person with the communication difficulty will find it hard to establish and/or maintain relationships.
In 1998 John Locke wrote that ‘small talk’ is crucial for the construction and enjoyment of relationships with others and that by revealing thoughts we elicit reactions from others. This is what we regard as social closeness or engagement. ‘Small talk’ or ‘social closeness’ may sound irrelevant but it is one of the most important purposes of human communication.
(Locke, J. L. (1998) “Where did all the gossip go? Casual conversation in the Information Age”, American Speech Language Hearing Association, 40, 3, 26-31)
Talking Mats, which uses attractive and motivating communication symbols, is one way to help people to express their thoughts and achieve ‘social closeness’, whether they are a 4 year old boy with Downs Syndrome or a 95 year old woman with dementia.
Talking Mats is one of the few resources that is versatile enough to be used as a stroke communication resource, for consulting children and young people or to help with communication difficulties and dementia, to name but three.
It allows people to express their thoughts in a visual way which in turn can elicit a response from their communication partner. Moreover, solid research has shown that Talking Mats increases engagement in people with different communication difficulties.
Click here to see our publications
Not many people enjoy going to the dentist but it can be a real problem for people with communication disabilities.
Recently I wrote about using Talking Mats in a care home to find out the views of an elderly lady with communication difficulties and dementia who had lost her dentures. click here. Using the mats, she was able to tell us that she was unwilling to open her mouth but thought that if someone was with her she might manage better.
Following our Talking Mats conversation the Care Home arranged an appointment with the dentist for the following week. Her son went back over what we had talked about just before the visit. She managed fine, opened her mouth and her treatment was carried out successfully.
Dentistry is a huge problem for many people, but the impact of not being able to cooperate can have serious implications for a person’s appearance, comfort, quality of life and health.
In preparing for a visit to the dentist it’s important that the person understands both what is going to happen and why its happening. Talking Mats is a visual tool that can help the person with communication difficulties both with understanding and also expressing their views. In this way the family and carers can find ways to reassure the person and support them to get the appropriate dental treatment.
Please let us know your thoughts on supporting people in similar situations.
The Talking Mats Team is increasingly asked to help ascertain a person’s capacity to express their views from a non-biased perspective. We are also asked to carry out service evaluations and are therefore developing independent consultancies to individuals and organisations. Our team of experienced Speech and Language Therapists, who have an in-depth knowledge of communication difficulties, are well equipped to do this.
The following are examples of independent consultancies which we have been asked to carry out:
- A lawyer asked us to work with a man who had had a severe stroke to ascertain his capacity to make decisions ranging from simple ones such as where he would like to go on holiday to complex ones such as who should control his finances. Using Talking Mats we were able to determine that he could make decisions about simple, concrete situations but wished his wife to make more complex decisions such as finances. check
- A Social Work department asked us to work with a woman with dementia and aphasia who had been sectioned. They needed to ascertain if she could understand why she could no longer live in her own home. We worked closely with her social worker and through using Talking Mats ascertained that she was unable to give informed consent.
- A Health Service facility asked us to evaluate the degree to which their patients felt involved in their care planning.
- A Care Home asked us to use Talking Mats with a 91 year old resident with dementia to find out her views about receiving dental treatment. There had been problems in the past and both the staff and her son were unsure if she understood the reasons and implications for dental treatment. Using Talking Mats, she was able to explain her thoughts about her teeth and dentures and clearly said that she was unhappy about opening her mouth for the dentist but that if her son were with her she would feel much better. We received this comment: “If you were to show the first few minutes without Talking Mats you would have thought this lovely lady lacked capacity, however the change and her engagement is noticeable.”
The following points explain with whom and how we can carry out the Talking Mats consultancy:
- Children or adults
- Family members, friends, professional staff
- Individuals or groups
- With or without a carer present
- At a venue and time which best suits the individual
- On any topic – we already have a comprehensive range of topics for both adults and children – but can create tailored symbol sets for any situation
- To find out someone’s views on a particular topic or situation at a specific point in time
- To help determine the capacity of an individual to make their own decisions
- To compare someone’s views over time
- To compare different people’s views e.g child and parent, person with dementia and carer
- We provide a detailed report with a copy of the person’s completed mat/s
To find out how we can help you and for discussion of costs please contact us at info@talkingmats.com or phone us at 01786 479511
“About half of all people with multiple sclerosis have some degree of problem at some time with aspects of thinking – memory, attention span or concentration. …. Many people may not recognise cognitive symptoms as an aspect of their MS and they can arise early in the course of the condition although the greater the disease duration and severity the more likely problems are to occur”. MS Trust
Talking Mats is one tool which can help people recognise any problems they may be having. It also provides a sensitive way for people to discuss these issues and plan ways to manage their situation.
We have developed a range of topics which encompass virtually all aspects of a person’s life
Insert mind map
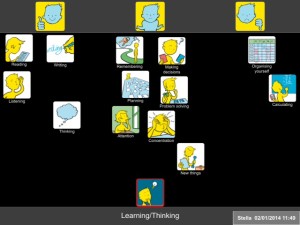
The Learning and Thinking topic is particularly relevant. The following is an example of a Talking Mat done with Stella who has MS and lives at home with her husband and 3 children.
Top Scale Used: Managing: Need some help: Not managing
Stella began by putting most of the option symbols between the Managing and Need some help columns. However as more symbols were presented, she took time and thought about each symbol more carefully and changed her mind about many of them.
She said that using Talking Mats helped her realise that she was having some problems. On completion of the mat, she showed it to her husband and together they discussed practical ways of ways of managing her difficulties.
There are a further 12 topics in the Health and Well-being resource that can be helpful to people with MS. these are available either on our app or as Talking Mats original.
I undertook the ‘Talking Mats’ on-line course to acquire a new skill and a way to enhance my communication with people with dementia in practice. I have found the learning strategies used are varied and interactive – so there is not a sense of sameness, even though visually there is a consistent layout to the presentation of each module (this expedites navigation). This enhances engagement and my interest so that I am never reticent in logging on to complete the next module! In the beginning, I felt that I could move a lot quicker through the course if the modules were available once each part was completed, instead of having to wait for feedback on each assignment. However, nearing the end of the training course, the benefits of this approach are now clearer. Spaced learning and spaced practice allows for thinking time and internalisation of the module components. In this way, I have come to appreciate the part skills involved in the overall process and how they come together. I now find myself observing the skills involved and the reactions of all communicating as well as the surrounding environment, body language etc. I have also found myself looking back over the past module materials to ensure I am integrating as I go and to remind myself of the rationales for the actions that need to be taken, as well as ensuring that I am more and more familiar with the new terminology that I have been exposed too.
Little did I know when I signed up that the benefits of learning about and how to use ‘Talking Mats’ would stretch wider than what I initially anticipated or wanted! In completing the course, I am now much more aware of my communication practice in general, and the part-skills involved. I can also now see the wide applicability of ‘Talking Mats’ to different populations, age groups and conditions. Communication is everywhere but it needs to be efficient and effective – I am now more confident that my communication practice will improve as a result of this course. For me this is the best outcome possible.
Please click here to find out how to book on the next course
When I went back to the Care Home where I was piloting our new Social Care symbols the staff told me this story about Ann (see previous blog). Apparently she usually is very quiet and never joins in with activities or with other residents. However when we used Talking Mats with the Activitiies symbols, she told me that she really likes singing and had started singing to me. Later that day, one of the care staff had suggested that she sing again and Ann started a song with him. Gradually other residents joined in and they had a lovely sing-song with Ann leading it!
On another day I used the Social Care symbols with Dorothy who tends to go off track and repeat stories over and over. She was quite sure about what she liked and didn’t like about the Care Home and using Talking Mats was a gentle and easy way to bring her back on topic.
I recently used the ‘Talking Mats Social Care’ pack in a Care Home with 3 residents, Ann, Barbara and Colin, who all have dementia. Neither Ann nor Barbara were wearing their glasses but all three were able to see and recognise the symbols and use Talking Mats to express their views. All three conversations took place in the lounge where the TV was on, staff were moving around and and where other residents were chatting.
Ann, whose mat is at the top of this blog, used the ‘Activities’ set and very quickly understood what to do although at times she needed to be reminded what the top scale meant. She said she was a very happy person and didn’t think I would find anything that she didn’t like but as we went through the symbols she became more thoughtful and said that she did not like DIY, exercise or knitting and sewing. She used the mid-point to indicate the things she used to enjoy but does not do now. She was delighted when she saw how positive her overall mat was.
Barbara used the ‘You’ set to tell me how she felt about herself. Although she could have placed the symbols, she preferred to sit back, tell me what she thought and let me place them for her. She felt fairly positive about most things although she was aware that her eyesight and her memory were not as good as they used to be. She also joked that she never had enough money.
Colin has dementia and is also profoundly deaf. He has only recently moved into the care home so we used the ‘Where you live’ set of symbols. Colin said several times that he didn’t think there was any point in having a conversation as he can’t hear. However after writing down the reason for doing it, he gradually realised that he could use the symbols to understand what I was asking and then express himself. He said he was generally happy with the Care Home although he missed his garden and found it hard to make friends now as he cannot hear what the other residents are saying. He also felt there are not enough activities that he can take part in. He mentioned that he has a pet dog but doesn’t know what has happened to it since he moved. One of the staff said he would try to find out. He seemed satisfied with the final mat and staff felt it would be useful to use Talking Mats more with him to reduce his isolation.
The following are thoughts from Jenni, a Psychologist who attended the Talking Mats Accredited training course.
‘Meeting with five colleagues from Sweden, England and various parts of Scotland for the accredited Talking Mats Training this month has been a fascinating experience. I have been accustomed to using Talking Mats with children and young people over the past seven years, and have seen the value of the approach in helping young people give their views for a meeting – particularly if they have communication difficulties and would struggle either through lack of confidence or skill to speak out when others are present.
However, we were not just a group who work with children and young people. Most came from health settings and examples were drawn from elderly patients, some with dementia, others with autism. As we shared our videos and told our stories it was obvious to me how relevant Talking Mats can be in those settings too. Some of the stories shook me. One person told how she was deep in conversation with a lady over her Talking Mat when the tea lady burst in, poured a cup of tea for the resident, asked if she was having a good time playing at puzzles, then left before any answer could be given. Time and again we found ourselves asking what is it about our institutions that puts routines above real communication and above proper respect for an individual.
In preparing a video to bring to the training I undertook a Talking Mat with my father, who is almost 90. It was a new kind of conversation for us both, but we were surprised – the structure allowed us to talk about what was going well and what needed a bit of an adjustment in domestic life and we both learned from the conversation. I think we will do it again!
Indeed, at one stage in the training we were asked to dream big and look at how we might want to take use of Talking Mats into new areas. I identified some good friends – one 91, one 101 and one 104 – where conversation can become rather one-sided. I am interested in the power of Talking Mats to help create a genuine dialogue when these friends are reminiscing, in other words, to help me to be not just a listener but to enter the dialogue. Having a record of the conversation will help us take the discussion further when we return to it.
As ever, the time spent with Talking Mats colleagues was refreshing, stimulating and I can’t wait to go home and try out some new ideas!’
Jenni Barr, Educational Psychologist
 Online training login
Online training login