Talking Mats are delighted to share that we have been awarded funding to create a brand-new sensory resource for children and young people who have Speech, Language and Communication Needs (SLCN) and sensory integration/processing difficulties. The funding to create this resource has been awarded by the Communication Trust from the Communication Consortium Grants Programme – funded by The Rayners Special Educational Trust.
The Communication Trust Consortium, a coalition of over 35 not-for-profit organisations, is hosted by ICAN. They harness collective expertise to support the workforce and commissioners to support all children and young people’s speech, language, and communication skills across the UK.
This exciting year-long project will be led by Laura Holmes, our Lead Associate for Children and Young People. Laura has been part of the Talking Mats Team since 2016 and has over 20 years’ experience of working as a Speech and Language Therapist with children and young people, across a wide variety of settings in both NHS and independent sectors.

New Sensory Resource
This project will develop, pilot and launch a Talking Mats visual communication resource to tune into a child’s view of their sensory needs. It will enable children and young people who have speech, language, and communication needs (SLCN) and sensory difficulties to have a voice in their therapy assessment, planning and intervention.
“Sensory integration” and “sensory processing” refer to the processes in the brain that allow us to take the signals from our senses, make sense of those signals and respond appropriately. Children and young people with sensory processing/integration difficulties often have speech, language and communication difficulties, which may be linked to a diagnosis of autism (Green et al 2016); developmental language disorder (Simpson et al 2020); hearing impairment (Alkhamra et al 2020); or a history of trauma (Fraser et al 2017).
This work is important as sensory assessments can typically involve a mixture of formal and informal questionnaires and checklists which are carried out with Parents/Carers, Education Staff, and may also involve observations of the child in their environment. The issue is that Child Voice is not always routinely, or effectively, included in these assessments, or in subsequent planning and intervention – however the Royal College of Occupational Therapists recommends that ‘person-centred goals/outcomes must be established prior to intervention’ (RCOT, Informed View: Sensory Integration and Sensory-Based Assessments 2021). This also links with the current SEND system in England and GIRFEC in Scotland, both of which also emphasise the importance of child voice throughout assessment, planning and intervention processes.
We plan to work with experienced Talking Mats OT and SLT practitioners working with children and young people who have SLCN and sensory needs, to co-create this resource.
Get Involved
If you, or someone you know, works with children who have a diagnosis of SLCN and sensory needs, and is an experienced Talking Mats practitioner, please share the news about this project.
If this applies to the work that you do, and you would be interested in taking part in this project, please follow this link to express your interest: Communication Trust Project.
Expressions of Interest should be submitted by Friday 23/09/22.
Stay Connected
For more information about Talking Mats, please visit our website www.talkingmats.com or follow us on social media to keep up to date with all our news!
By Nyaka Mwanza
Multiple sclerosis (MS) can result in a variety of communication difficulties. While broaching uncomfortable topics, such as multiple sclerosis life expectancy, can pose its own challenges, MS can also physically disrupt some people’s ability to communicate as effectively as they once did.
That’s because MS is an immune-mediated condition that damages and destroys neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). Known as demyelination, this destruction of nerve cells causes lesions in the spinal cord, optic nerves, and brain. MS lesions in certain areas of the CNS can sometimes result in difficulties with speech and comprehension. However, there are ways of overcoming these difficulties so that a person may communicate better.
How MS Disrupts Information Exchange
Communication issues in people with MS usually arise due to damage in areas of the CNS that are responsible for cognitive and motor function.
Cognitive Impairment
Cognition refers to our ability to think, read, learn, remember, reason, and concentrate. Cognitive processes also comprise language, planning ahead, imagination, and perception.
Approximately 70 percent of people with MS experience impairments in these cognitive functions. Cognitive difficulties such as slower processing speeds and worsened memory can impede a person’s ability to process spoken or written language. Cognitive impairment in a person with MS may also look like difficulty finding the right words for things when speaking, difficulties spelling words correctly, or switching words incorrectly when speaking.
Language and Speech Difficulties
Speech and language involve several cognitive functions, but speech also involves intact motor function, especially the coordination of the muscles in the lips, tongue, vocal cords, and diaphragm. However, MS can disrupt the brain’s ability to communicate properly with various muscles in the body, sometimes interfering with the ability to produce appropriate speech.
Dysphonia is a voice disorder due to weakened diaphragm functioning. The diaphragm helps with breathing and volume control. Dysphonia can result in very quiet or loud speech. A person with dysphonia may also find that they run out of air while talking. Dysphonia can also cause a raspy voice.
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder commonly caused by the weakening of muscles used for speech, swallowing, and breathing. Between 40 and 50 percent of people with MS experience passing or permanent dysarthrias, which may result in slurring, monotone, and disruptions to speech patterns with abnormally long pauses between syllables or words. Issues like these can make holding a conversation difficult or uncomfortable.
Bridging the Communication Gap
A speech or language pathologist is a specialized healthcare provider who can evaluate and help treat voice and speech disorders. Depending on the severity of a person’s MS, some speech therapy will focus on compensating for dysfunctions in cognition and speech and enabling people with MS to find alternative means of communication. Other therapy for more mild speech difficulties may focus on developing strategies to control breathing, strengthen the vocal cords, or even simplify speech to make it easier to get through. People with MS may find it’s easier to hold a conversation when they’re not competing with other noises or distractions. Tools that aid with cognitive dysfunction, such as Talking Mats, can help loved ones concentrate on common topics to help make discussion easier. Here is an example of how Talking Mats helped some with multiple sclerosis to set their goals https://www.talkingmats.com/getting-root-problem/
References
- MS Prognosis: Multiple Sclerosis Life Expectancy
- https://my-ms.org/anatomy_nervous_system.htm
- https://my-ms.org/mb_cognitive.htm
- Speech and Swallowing
- Multiple Sclerosis and Communication Difficulties – East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust
About the Author
Nyaka Mwanza is a freelance writer for MyHealthTeams. She completed a B.A. in Communications: Visual Media from American University and undertook post-baccalaureate studies in Health/Behavioural Communications and Marketing at Johns Hopkins University. Nyaka is a Zambian-born, E.U. citizen who was raised in sub-Saharan Africa and Jacksonville, N.C. However, she has called Washington, D.C., home for most of her life. For much of her career, Nyaka has worked with large global health non-profits focused on improving health outcomes for women and children. Nyaka believes words hold immense power, and her job is to meet the reader where they are, when they’re there.
Thanks to Kate Boot for the second part of her interesting blog describing her use of Talking Mats to assess and teach understanding of concepts and vocabulary related to Relationships and Sex Education, illustrating use of Talking Mats in a teaching context. Check out the first part of her blog here: https://www.talkingmats.com/sex-and-relationships-part-one/
In the second part of this two-part blog series, I explore how using Talking Mats enables us to review the progress of linguistic and pragmatic understanding within the context of Relationships and Sex Education.
Considering the speech and language therapist’s focus is on increasing a person’s linguistic and pragmatic understanding we also use talking mats to explore potential target vocabulary and concepts. Drawing on the best evidence-based practice from the developmental literature (Steele and Mills, 2011; Justice et al, 2014; Lowe et al, 2018) we need to use a variety of methods to teach the underpinning vocabulary which wider RSE concepts relate to or hinge upon, e.g., safe, consent, power and control.
Using Talking Mats enables me to assess what the student already knows or understands of the vocabulary, which in turn informs the ongoing therapy programme, e.g., the degree of prompting or support needed to learn new words and to apply them to situational contexts. We repeat these activities throughout the academic year to evaluate how well the therapy programme is going and how the young adult’s understanding is developing.
Thinking back to Young Adult B from the first part of this blog, from their initial assessment, it was evident that they did not understand the word ‘safe’, therefore applying the evidence base described above we spent one term working on developing their understanding using a variety of communication friendly strategies. They even wrote two songs about the word ‘safe’ to the tune of Jingle Bells and Ariana Grande’s ‘Thank u, next’. Towards the end of the term, we completed a talking mat activity to review their progress. As I referred to in Part One it’s important to give control to the ‘thinker’, it is their mat.
Moving forwards, we will continue to review their progress using Talking Mats, which combined with the data from other best evidence-based practice will be used to determine the increase in their word knowledge which in turn, should develop their self-awareness and improve their skills needed to make decisions about sexual relations.
Kate Boot is Clinical Lead, Specialist Speech and Language Therapist and Sensory Integration Practitioner at Phoenix Learning and Care. To share ideas or chat further about this work you can contact her via Twitter @SLTinSEND or LinkedIn www.linkedin.com/in/kate-boot-salt
References
Justice, L. M., Schmitt, M. B., Murphy, K. A., Pratt, A., & Biancone, T. (2014). The ‘robustness’ of vocabulary intervention in the public schools: targets and techniques employed in speech–language therapy. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 49(3), 288-303.
Lowe, H., Henry, L., Müller, L. M., & Joffe, V. L. (2018). Vocabulary intervention for adolescents with language disorder: a systematic review. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 53(2), 199-217.
Steele, S. C., & Mills, M. T. (2011). Vocabulary intervention for school-age children with language impairment: A review of evidence and good practice. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 27(3), 354-370.
Many thanks to Professor Anna Dunér, Dr Angela Bångsbo and Associate Professor Tina Olsson for this guest blog describing their research project where Talking Mats will be used to enable service users living with dementia to be involved in decisions about their home care services. The project is based on a collaboration between Department of Social Work at the University of Gothenburg, Borås University College and the municipality of Borås, aiming to develop and evaluate the use of Talking Mats.

In Sweden, as in many other developed countries, ideas of consumer choice and personalisation of services have been implemented in social care with the intention of achieving better choice and control as well as increased quality of the services provided for the individual. However, persons living with dementia are at risk of being excluded from the opportunities provided to other groups of service users. Thus, it is important to develop both needs-assessment procedures, and improve the performance of home care services, to enable older people living with dementia continuous choice and control in their everyday living.
We hope that Talking Mats will improve the communication between service users, care managers and staff in eldercare and lead to increased influence of service users over the decisions and planning of their home care services.
During 2020 we have funding for a planning study where we can develop and test the Talking Mats decision aid, identify, translate and test outcome measurements, and refine and test the procedures for a comparative intervention project. In 2021 we hope to attain funding for a three year study.
We have already received valuable advice and information about Talking Mats research from Dr Joan Murphy and hope to keep in contact with her and the Talking Mats team throughout our project.
If you are interested in Talking Mats Research, check out our recent blog with details of how you can get involved with our Virtual Network:
https://www.talkingmats.com/virtual-talking-mats-research-network-launched/
In the first of two blogs, we talk about how using Talking Mats Resources can help people have better conversations.
Talking Mats provides a visual framework to help people express their views and feelings, using a selection of communication symbols that cover a variety of topics. Talking Mats resources are used by many professionals across a wide range of health, social care, residential, and education settings. Most of our resources are available in both low-tech, and digital, formats. In this first blog we focus on the resource bundles which are available to purchase with our Foundation Training course.
Our resources are available to buy through our website (https://www.talkingmats.com/shop/) however we do strongly recommend completion of one of our Foundation courses (https://www.talkingmats.com/training/foundation-training/) to get the most benefit from Talking Mats – and to use it to its full potential. If you add a Health and Wellbeing, Consulting Children & Young People, or Social Care resource pack bundle to your training you only end up paying £65 for the training day itself which is a great deal!
Resource Bundles available to purchase with Training
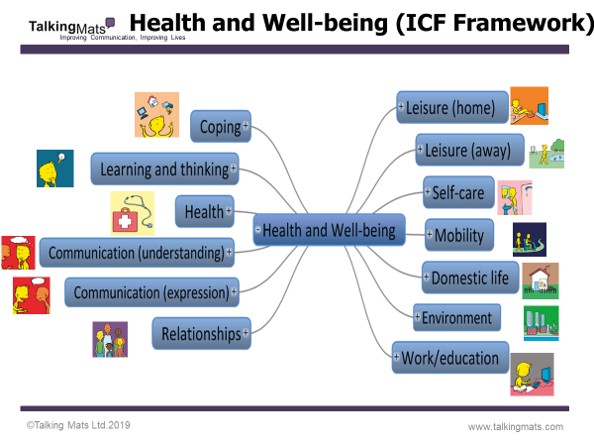
Health and Wellbeing Bundle:
These packs are based on the ‘activities and participation’ domains from the WHO ICF framework and includes 9 topics which are relevant to people, regardless of their health, disability or where they live around the world. We have translated these into more ‘user-friendly’ language and have generated symbols to represent each topic.
In addition to the 9 topics from the Activity and Participation domains, we have also included Environment and Health, which are important topics within the ICF framework and in people’s lives.
Consulting Children and Young People Bundle:
These packs are based on ‘Getting It Right For Every Child’ (GIRFEC), a Scottish framework for everyone to use when working with children and young people. There are three broad topics which are relevant to any child or young person’s life. This resource can also be used with SEND reforms in England. There are different packs for each developmental stage: Early years (ages 3 to 7); Primary (ages 7 to 12) and secondary (age 13 upwards).
Best Value Bundle: This option includes the Health and Wellbeing and Consulting Children and Young People bundles above, as well as our Social Care resource packs, providing a complete set of resources to support communication on a comprehensive range of topics for children and adults.
If you’d like to book a place on one of our Foundation Courses and would like to know more about our bundle options, get in touch with us at info@talkingmats.com
Find out more about our Foundation Training course here: https://www.talkingmats.com/training/foundation-training/
Many thanks to Charlotte Phillips and Laura Douglas, SLTs at Blossom House School, New Malden, for this latest guest blog which looks at how Talking Mats are used for therapy goal setting within the context of a specialist school for children with SLCN. Further information can be found on their RCSLT Poster Presentation (September 2019) here – AAC Poster RCSLT Conference September 2019
Goal setting can be a labyrinth to navigate! Do these goals reflect the pupil’s own views? Is there a discrepancy between staff and pupil ideas for goals? Are these goals motivating? Are the goals functional? Are pupils avoiding goals they would like to achieve for fear of failure? Add to this the language rich dialogue required in order to establish goals and similar to a maze you may encounter dead ends, twists, turns and a feeling of entrapment. How can we ensure we do not assume needs and that the goal setting process is collaborative and person-centered? Enter Talking Mats; a tool which enables you to make sense of the maze, like the lookout tower in the middle it allows you to have a clear view of how everything fits together. You’ll now find the goal of exiting is far easier!
How can Talking Mats help?
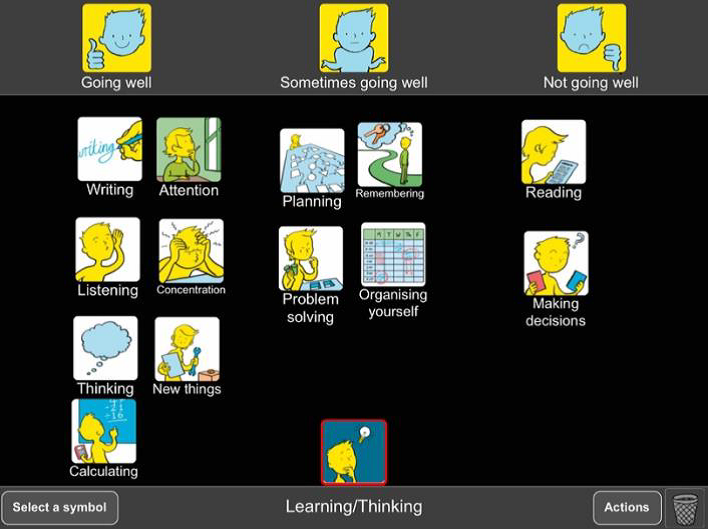
At Blossom House the Talking Mats framework is utilised at the beginning of therapy to support pupils with DLD and specific learning difficulties to identify areas of their strengths and needs and develop personally meaningful goals that are associated to these areas. Some of the pupils are competent verbal communicators within a social context but due to the emotive subjects they may be exploring they may not be able to access these skills within therapy. Talking Mats are also used to baseline students’ self-awareness alongside prompting pupil voice. Talking Mats are tangible and have low linguistic demands which allows students with kinaesthetic and/or visual learning style preferences, and communication needs to engage in these discussions.
Case Study 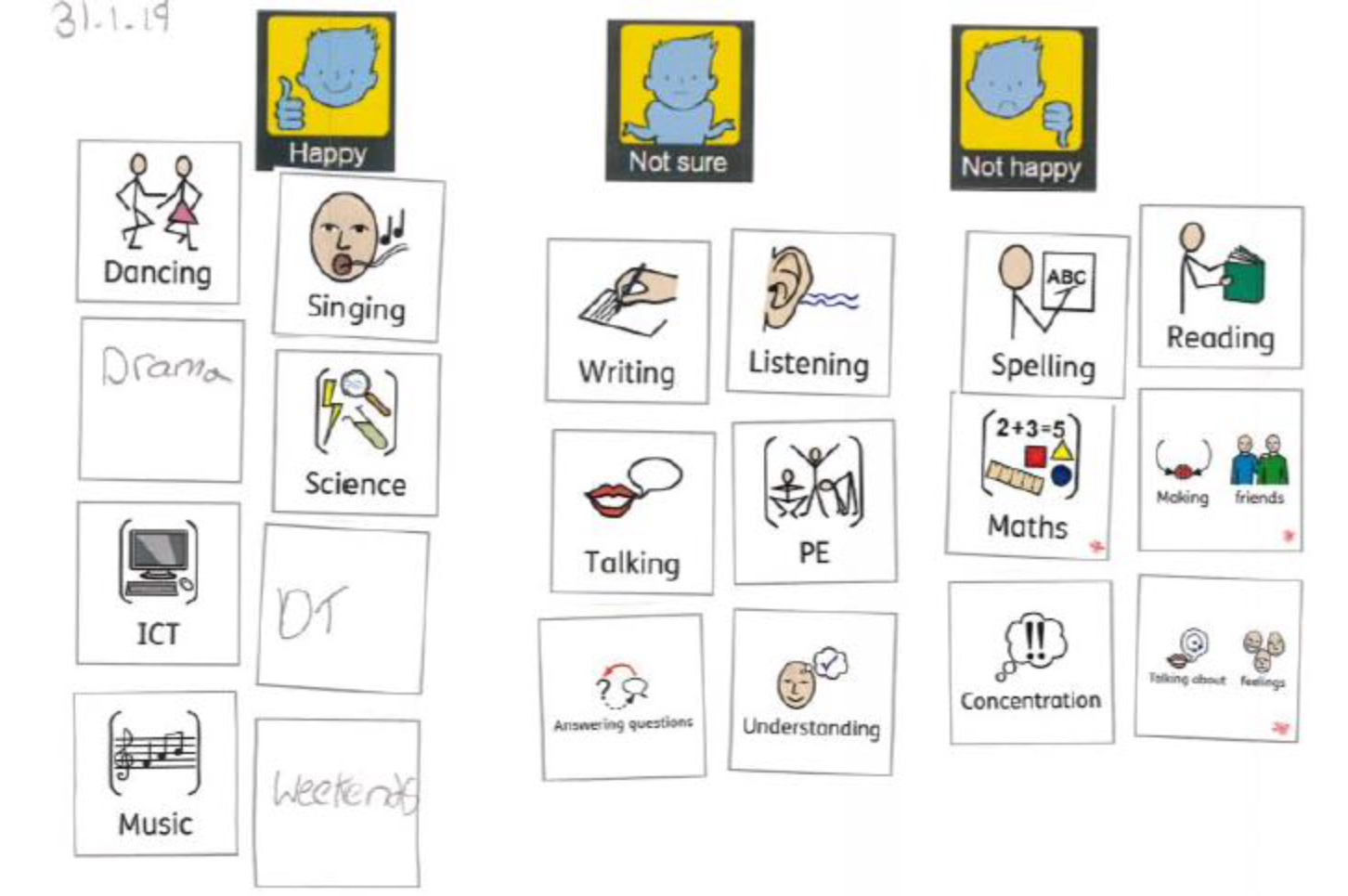
Next Steps
The school would now like to embed Talking Mats as a whole school approach. The first step will be Talking Mats forming a core part of School council meetings to ensure that every pupil has a voice. There will be consultation with SLTs around integrating Talking Mats into the Annual review pupil voice protocol and into therapy outcome measures. This will be facilitated through the use of the digital talking mats package which allows for staff to create mats with pupils on the move, with minimal resources. These can then be emailed to staff and pupils which makes this information practical for staff to use within the context of their extremely busy school day. The use of technology to facilitate self-advocacy is an interesting field which needs further investigation.
If you are feeling inspired and would like to access Talking Mats training to enable you to introduce a similar approach in your school take a look here –
https://www.talkingmats.com/training/foundation-training/
To find out more about our resources, including our Digital Talking Mats app, check out this link here –
https://www.talkingmats.com/shop/
In our latest blog, Rachel Woolcomb, Talking Mats OT Associate, discusses how Talking Mats can support Reflective Practice for Occupational Therapists.
Taking time out to stop and reflect on our practice can be a challenge. We convince ourselves there are more important things to do, people to see, targets to meet, and therefore we just don’t have the time.
However, I suggest, that with this mind set we are doing ourselves, and the people to whom we provide support and care, a disservice.
Clinical supervision has always been embedded in the culture of occupational therapy and at its best should create a safe and supportive environment in which reflective practice can take place.
Unfortunately, in practice, the reality can look different.
The more I have used Talking Mats to enable my clients to think and express their opinions, the more I have been convinced, that there is also great benefit to them being used within the clinical supervision process.
I want to thank the occupational therapists who agreed to explore this further with me. They used Talking Mats to think about their coping skills at work, or reflected on how their ability to learn and think, impacted their job role.
They were surprised how easy they found it to think about the full breadth of their working life and the impact this had on their wellbeing. As clinicians, we are great at looking after other people and ensuring that their health and wellbeing needs are met, however, we are not so great at caring for ourselves.
The latest TMOT resource provides more information about why and how, Talking Mats can be an effective tool in enabling a reflective thinking space for clinicians. Check it out here: TMOT3 Reflective practice
Give it a go… You are worth it!
To find out more about our Talking Mats resources, check out this link:
https://www.talkingmats.com/shop/
Many thanks to our Talking Mats Founder, Dr Joan Murphy, for this latest blog talking about the training course she recently delivered at the Cyprus University of Technology.
Cyprus is a beautiful Mediterranean island with a population of approximately 1 million.
I was invited by Dr Eliada Pampoulou to run a 2-day course on Talking Mats for 12 Speech and Language Therapists, some of whom are masters students and some, lecturing staff at the Cyprus University of Technology. The Cyprus University of Technology founded the first Department of Rehabilitation Sciences in Cyprus and the Department offers the first public recognised university bachelor degree in Speech Language Therapy / Speech Language Pathology in the Greek language (https://www.cut.ac.cy/faculties/hsc/reh/).
Day 1 was a Talking Mats foundation training course and Day 2 focused on discussion around capacity, research and clinical applications. This model worked very well as the participants were able to think about and discuss how to apply the training immediately.
Some of the immediate plans of the participants were both clinical and research oriented and are outlined below:
- To administer the Greek Stroke and Aphasia Quality of Life Scale (SAQOL-39) with healthy people over 50 both with the text version and an adapted Talking Mats version quality and to examine which they prefer.
- To use Talking Mats both with people with people with aphasia and their carers in order to share their understanding about the communication skills and needs of people with aphasia.
- To use Talking Mats as a tool to identify the factors that are related to AAC system acceptance or abandonment by focusing directly to the views of people with complex communication needs
- To use Talking Mats as a goal setting tool for both paediatric and adult population
- To use Talking Mats to gets clients feedback about therapy services
- To use Talking Mats for student appraisals regarding their clinical training
Dr Eliada Pampoulou has created the first Talking Mats centre in Cyprus which aims to gather all people who received training every few months to share their experiences and support each other to embed Talking Mats in practice and research.
We hope that Eliada will come to Stirling next year to gain her Talking Mats licence to enable her to train others and extend the reach of Talking Mats even further.
We regularly run our Licensed Trainer 2-day courses at our base in Stirling – if you have attended Talking Mats Foundation Training and would like to train other people find out more here:
https://www.talkingmats.com/training/train-the-trainers-accredited-training/
Many thanks to Lynn Blair, SLT (NHS North Lanarkshire) for writing this guest blog describing a recent project in which she and her colleagues used Talking Mats to gather the thoughts of secondary-aged pupils with social, emotional and behavioural support needs:
Do you remember your school janitor? Was he/she a cheery soul who you enjoyed talking to? Perhaps there was another member of school staff who you trusted and felt you could chat with. Secondary school can be a challenging environment for any teenager, let alone those who have speech, language and communication needs (SLCN). Young people need adults in their lives who they can feel at ease talking with.
The purpose of our recent project (See Lanarkshire SLT SEBN Poster 2019 and Lanarkshire SEBN Project Summary) was twofold. Firstly we wanted to find out how many of the young people in our local secondary schools for pupils with social, emotional and behavioural needs (SEBN) had language and communication difficulties. We also wanted to hear about the impact of those support needs by gathering the thoughts of the pupils themselves and that’s the focus of this blog.
We have to admit we were a bit anxious before we met with the pupils. Would these young men and women even give us the time of day with our friendly faces, mats and pictures? In the actual event, for the most part the tool was met with curiosity and then full engagement. The young people quickly grasped the idea. Some did not speak at all as they placed the images and others used the opportunity to tell us a great deal about how they felt about talking to different people in their lives and in different settings.
The information that we gathered is now being used to plan evidence-based speech and language therapy services to the school and young people. The use of Talking Mats gave us interesting information like the fact young people felt auxiliary staff such as janitors and assistants are often easier to talk with than teachers and as a result, we are thinking about how we involve all school staff in future events.
We are only too aware that the young people we met have often felt excluded from other people and from certain places. Talking Mats gave them the opportunity to be heard and we’re excited to consider how we can use them in the next phase of our work to support their communication needs.
If you are feeling inspired and would like to find out more about accessing Talking Mats Training – check out this link here: https://www.talkingmats.com/training/
Many thanks to Dr Sally Boa, Head of Education, Research and Practice Development at Strathcarron Hospice in Stirlingshire, for this latest guest blog – linking to her great presentation at our TM is 21 event in August. Sally’s presentation – Talking Mats and Palliative care – focused on using Talking Mats in Palliative and End of Life Care, and included information about the Talking Mats ‘Thinking Ahead’ resource – here Sally shares her own experiences:
Talking about death and dying and making plans for the future is difficult to do. This is partly because no one likes to think about their own mortality and partly because as a society we don’t talk about it. I work in a hospice where people are encouraged to talk about the care and treatment they would want as their condition deteriorates. Even here, these conversations can be difficult, particularly if someone has communication or cognitive difficulties, if there is uncertainty about prognosis or if there are different opinions within the family. The ‘Thinking ahead’ Talking Mats resource is a great tool to use to enable these conversations to happen. In my presentation at the ‘Talking Mats is 21’ event, I provide some background about how the resource was developed. I have used it to support those with communication difficulties to have a voice and also with people who simply find this a difficult topic to think and talk about. Use of the Mats helps people to think through the issues one at a time and see for themselves how they feel about things in relation to one another. Most importantly, it helps open up the conversation about the future and helps people to prioritise and see for themselves what they need to do in relation to making plans for the future. Then they can get on with living and doing the things that are most important to them.
A most memorable example of using Talking Mats with someone towards the end of life is when I was asked to work with ‘Gill’ who had severe communication difficulties. I used the ‘Thinking ahead’ resource with her and found out that she had made many plans in relation to sorting out her affairs (e.g. power of attorney, funeral arrangements). She hesitated when I showed her the ‘making memories’ symbol and at the time I couldn’t work out why. To finish the session, I used the ‘indoor interests’ symbols with Gill and we had a great conversation about all the things she enjoyed doing. When I gave Gill the ‘arts and crafts’ symbol, she became really animated, and was able to tell me that she wanted to finish creating a memory book of photos that she had been making up for her family. Using the Mats, Gill managed to convey why she had hesitated with the ‘making memories’ symbol. Following on from this, we had a conversation with the hospice creative arts coordinator who was able to support Gill to complete, not only her memory book, but also other creative pieces. In her last few days of life, Gill was able to identify and work towards really important goals and left some amazing memories for her family.
To find out more about our Thinking Ahead resource, which is available to those who have accessed our Foundation Training – follow this link – https://www.talkingmats.com/product/thinking-ahead/
If you haven’t accessed our Foundation Training yet – find out more here https://www.talkingmats.com/training/foundation-training/
 Online training login
Online training login