In Stockport we have a termly ‘Voice of the Child/Young Person’ Champions Network meeting during which professionals working in health, education and social care settings across the area meet to discuss real-life examples and to share information and strategies – during the last meeting in October 2018, we discussed using Talking Mats to support police interviewing.
Louise Tickle, Specialist Learning Disability Nurse from the Children’s Learning Disability Team at Stockport NHS Foundation Trust, shared a great example of using Talking Mats to support a child she was working with to share information about a serious safeguarding concern. Louise had been asked by the police to carry out a Talking Mats session with the child as they were aware that she was already using this approach. Louise led the session and was supported by the child’s school SENCO, who had also been Talking Mats trained. The aim was to explore a disclosure which the child had previously made.
Louise shared some great tips about using Talking Mats during an investigation phase:
- Introduce the Talking Mat with a familiar topic, then move on to the main topic/ area of concern
- Watch out for non-verbal cues – initially, the child appeared to be happy and relaxed during the interview, however the child’s non-verbal communication visibly changed when the topic changed. It is easier to pick up on these non-verbal cues if you are able to video the session.
- Have another Talking Mats trained observer present if possible to support and evaluate the session with you.
- Make sure you use terminology that the child is familiar with, and use language that the child would use themselves e.g. when describing body parts.
Talking Mats are often used by people working within the justice system, including registered intermediaries – here is the link to one of our previous blog posts for more information: https://www.talkingmats.com/talking-mats-used-court/.
In this work you must be clear about the different stages of safeguarding and follow the procedures within your organisation. Disclosure and investigation are two different phases. The Keeping Safe resource has been trialled and tested to support people to raise concerns. https://www.talkingmats.com/keeping-safe-a-new-talking-mats-resource-available-to-purchase/ . When a disclosure moves to the investigation phase you may have to personalize the mat to fit the situation but what is key is that you keep the options open and non-leading.
For further information about accessing one of our Talking Mats Foundation Training Courses across the UK, and our ‘Keeping Safe’ Advanced course, see our training options here https://www.talkingmats.com/training/
Find out about the Core and Essential Service Standards for Supporting People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities. and thanks to Joanna Grace for this interesting and important guest blog ,she writes;
Last week I threw used deodorant canisters at an audience of earnest professionals and was cheered for doing so. What was going on?
I run The Sensory Projects an organisation that aims to share the knowledge and creativity required to turn inexpensive items into effective sensory tools for inclusion. In all I do I am working to contribute to a future where people are understood in spite of their differences.
The empty deodorant canisters had been washed, their roller balls removed to enable me to fill them with festive scented balm – some frankincense some myrrh – with balls replaced they make wonderful massage tools enabling me to form a connection through touch and smell with persons of all abilities and to share a sensory conversation around the season.
I lobbed them at my audience to bring to life the new Core and Essential Service Standards for Supporting People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities. That title might not sound exciting and the link with my improvised massage tools might not be immediately apparent but I promise you the link is there and the document is very exciting indeed.
My original dream when I set up The Sensory Projects was to write five sensory stories. That dream was a bit of a fantasy and so I had to pinch myself when it came true. The original five stories are sold to fund the writing of more and there are now twenty available on the website. The stories led to books, of which there are five in print currently and a few more in the pipeline. The stories project led to another project, which led to another, and there are four currently and a fifth due to start next year. Through the projects I have had the chance to do some remarkable things and found myself in situations I never imagined I would be in: I’ve been featured in a book given away in Lush stores globally, I’ve been interviewed on Radio 4, I’ve done a TEDx talk, I’ve even exchanged text messages with the Foo Fighters! If I continued to pinch myself when remarkable things in my life happened I would be black and blue by now.
And yet of all of these wonderful things and the many adventures I have had, by far and away the best thing I have been a part of is the new Core and Essential Service Standards for Supporting People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities.
The new Core and Essential Service Standards for Supporting People with Profound and Multiple Learning Disabilities is a document that describes what best practice care looks like when supporting people with profound and multiple learning disabilities. It is beautifully simply having just 7 standards for what best practice looks like at an organisational level and 6 standards for what it looks like at an individual level. It was written by a team of volunteers over 140 strong over an 18 month period. It represents an enormous work of effort and hope. I am humbled and proud in equal measure to be one of its four lead authors. If adopted by the inspecting agencies it would change the face of what care looks like for individuals with complex disabilities nationwide and influence care provision globally.
Even without being adopted by the inspecting bodies it is having an impact. I encourage all settings to take a look at it. If you are a great setting celebrate that you meet the standards, declare it publicly, display it on your website, tell the world – and help us to create an expectation that this is what care should look like. If you are a middling setting celebrate that you are working towards the standards, use them as a reflective tool to drive up the quality of care that you offer. And if you work in a duff setting….well, I spoke to one woman who worked in a setting where the management were thoroughly uninterested in supporting their residents with profound and multiple learning disabilities. She looked through the document, thumbing the forward by Norman Lamb and the endorsement by NHS England, she gave me a wry smile “I don’t think my boss will know this isn’t legal” she winked, “I’m just going to give it to him!” However the change comes about, we want to see these standards upheld.
Early on in the writing process we had to make a decision: were we going to describe what best practice care looked like now, or what it ought to look like. We went with what it ought to look like. This is an aspirational document. But that is not to say it is unachievable. I cannot emphasise the “ought to” strongly enough. The first standard for individuals is communication, within the explanation for this standard is the following: “Communication should be a collaborative activity, it has to be a two-way exchange; reciprocal and responsive.” That is not asking a lot. It is a shame on our society that such basic standards are aspirational at all. It should already be happening.
We launched the standards at an event called Raising the Bar last year. Raising the Bar II was held this year and looked at how far we had come since the launch. One speaker told the room full of delegates “before you seek to raise the bar you must allow family members to say where the bar is currently” and we did. Families presented about the level of care their loved ones had received and their stories were horrific to hear. The bar is currently set very very low. Standards such as two way communication are aspirational. It is so low that it should be easy to raise. Simply by being aware of what we should be doing, making others aware, and expecting to see positive change we can go some way to improving care. Raising the Bar III is due to be held at Birmingham University next year on the 25th of October.
Most importantly of all we want families and primary carers to know about the standards so that they can use them as an advocacy tool and demand that settings meet them. There is a community of practice hosted on Facebook that networks people working together to see this change come about. Please join us.
So what was the deodorant canisters thing about? Well a two way communication for someone who does not use words can begin at a sensory level. It can be me massaging your hand with a festive scent and watching for your response. To be truly two way I need to share this time with you on multiple occasions as your responses today might be indicative of something other than your opinion of this scent. They could be a pain in your stomach, a tightening of a muscle, a epileptic shudder. To truly know your response, your opinion, to truly make the communication two way I need to repeat, and to give you time, and to tune in to your response and then I need to listen to it and act upon it. If through our conversations you tell me you like one smell and dislike another then this will help me choose from the pile of toiletries you are given for Christmas which you will really enjoy. As I share these simple conversations with you over time I address another of the standards:
Standard two is about health and wellbeing and describes how staff will have an awareness of what good mental health looks like for an individual and how to support it. Smell has a particularly powerful effect on the emotions and fostering an engagement with smell is a good way of supporting someone’s mental health – regardless of their ability, disability or neurodiversity. On my Sensory Engagement for Mental Well Being training day I look at many simple sensory strategies for supporting mental health for people with complex disabilities.
A document like the standards can seem dry and impersonal, throwing things at my audience helped me to bring it to life. My whole working life, and much of my private life – I have worked for inclusion in mainstream education settings, I have taught in a school for children with severe and profound special educational needs and disabilities, I have inspected schools for their provision for children with additional needs and provided consultancy services to schools looking to improve their provision, I have family members with neurodiverse conditions and physical disabilities, I have been a registered foster carer for children with severe and profound special educational needs and disabilities and I have run The Sensory Projects – has been about working to see people be better understood, better included and better appreciated for being themselves. The Standards are the pinnacle of all of this work.
You can download the Standards for free from the PMLD link website: www.PMLDlink.org.uk by following the ‘Resources’ tab, or from my own website www.TheSensoryProjects.co.uk – again follow the Resources tab. Please print them off and share them far and wide, make sure everyone you know who is involved in the lives of people with profound and multiple learning disabilities, or has influence over their lives in anyway, knows about them. Together we will create this change.
I also warmly invite you to join us on the Community of Practice, let us know who you have shared the Standards with, it is great to hear what others are doing.
Grateful thanks to Prof. Dr. Norina Lauer, OTH Regensburg – University of Applied Sciences, Germany for this blog.
At the conference of the German Society for Aphasia Research and Treatment (GAB) from the 1st to the 3rd of November Franziska Rau presented a poster – Let pictures talk – about her bachelor thesis on Talking Mats.
Speech and language therapists from German-speaking countries meet at this conference to present their latest research findings. This year’s theme was ” Aphasia Therapy Digital”.
The presented bachelor thesis about Talking Mats was performed at the HAN University of Applied Sciences, Netherlands, and was written by Franziska Rau together with Karoline Bitter and Lara Stobrawe. The students asked 29 people with aphasia and 63 people without aphasia for how representative they rated the images and terms used in the Communication section of the Digital Talking Mats Health & Well-being resource. While the healthy persons judged many items as not clear enough, the people with aphasia estimated significantly more pictures and names as appropriate. For this purpose, various reasons have been discussed, such as the possibility that the persons with aphasia directly perceived the pictures and terms as aids, while healthy persons judged more critically on the basis of the task. But also problems of concentration or comprehension in people with aphasia would be causally conceivable. This should be examined in further studies.
The poster was presented as part of a poster session and was well received by the audience. Thanks to Franziska, Karoline and Lara for their great study and to Holger Grötzbach, Janine Coopmans and Xaver Koch who supported the students.
We are always happy to receive projects and posters from anyone studying how Talking Mats can be used
Did you know you can get a student discount on Talking Mats courses?
- Just started / started back on your College or University Course?
- Looking to have a certificate in understanding and using an award winning communication resource on your CV?
- Or perhaps you are teaching a course centered around communication ?
- Did you know that students can get a 20% discount on our Foundation Training Fees?
We run face to face full day training courses in various venues in England and two ½ day sessions in our base in Stirling.
Our Online Foundation Training runs on a 6 weekly programme making it a flexible and accessible way to learn how to use Talking Mats.
Once you have completed the Foundation Training you are eligible to buy symbol packs at a reduced price letting you build up your Talking Mats resource that you can take with you to your first job!
There are limited places per course so it is first come first served!
Read Rosie Murray’s great blog. She trained in Talking Mats as a student and is now using it in her role as a Speech and Language Therapist working in a college for young adults with autism, learning disabilities and SEBD. Plus she has now gone on to become a Talking Mats accredited trainer
We are very grateful to Elena Maxheimer, a Speech and Language Therapy student from Germany, for sending us this blog of a summary of her thesis which examined the use of the German Digital Talking Mats with people with aphasia.
In May 2018 I did my bachelor thesis on the German version of the Talking Mats app. Under the consultation of Prof. Dr. Norina Lauer, I delivered two workshops for eight people with aphasia. In these workshops the participants practiced doing Talking Mats and afterwards they evaluated the app by filling out a short questionnaire and taking part in a focus group in which they discussed the app’s content and practical use.
The participants generally rated the app as useful for people with aphasia and in particular, the topics, pictures and terms were rated as suitable for people with aphasia. The two most chosen topics were Health and Communication. Some aspects were difficult for people with aphasia. Some of the group had problems in choosing a suitable scale, writing on an empty card or writing down comments.
Suggestions for modification were
– Showing two sessions of Talking Mats parallel to have a better comparison
– Using the app on the smartphone – however the screen on a smartphone is too small to be manageable
– Saving the login data, so you don’t have to login every time you use the app
– One older participant suggested additional topics about specific diseases such as diabetes
– Another younger participant wanted more about sex, feelings, sympathy and love.
For other information about Talking Mats in Germany click here
Also Joan Murphy and Norina Lauer will be running a Talking Mats workshop in Cologne on May 5th and 6th 2019
Talking Mats received funding from The Health and Social Care Alliance Scotland to look at how using the Digital Talking Mats can help people with long term conditions, including dementia, to manage their health and well-being and to recognise their own strengths and abilities. We also hoped that participants would be able to have more control over their lives and have improved communication with families and professionals.
11 people living with dementia and their partners were involved in the project. Each participant had a tablet device and was given a personal digital Talking Mats licence which gave them access to 13 topics in the Talking Mats Health and Well-being resource. We visited each participant at home, taught them how to use it and asked them to complete at least 1 digital Talking Mat per week for 6 weeks on any topic they wished. The design of the digital Talking Mat allowed them to email their mats directly to us. We visited each participant a second time to discuss how easy it was to use the digital Talking Mats and their views on their completed mats. We asked those who wished to, to continue sending us completed mats beyond the initial 6 weeks and we visited them again in 6 months to discuss how they were managing.
In total we received 94 digital mats across all 13 topics from the participants living with dementia who reported that the use of the Digital Talking Mats during this project gave them a better understanding of their own individual health and social care needs.
A woman with dementia said ‘It (Health mat ) made me realise things are not so bad and made me think I will continue with my exercise classes, carry on walking, socialising and eating well’
As well as helping participants self-manage their lives, an unexpected outcome of this project was that many people found that using the Digital Talking Mats helped them see the positive things in their life and not just the negative. It also highlighted that despite having a deteriorating illness, things were not getting worse.
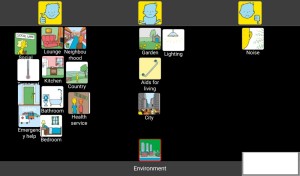
‘This mat (Environment) showed me how happy I am in my own home and my neighbourhood’
The following are some of the comments we received throughout the project.
• It helps me sort out my thoughts – very useful
• I get so much out of the process
• I come up with insights which might help me in the future
• I can now talk to (my wife) in a way I couldn’t before
• I’m more relaxed now
• I come up with niggly health things that my partner didn’t know
‘It made me realise things are not so bad’.
If you know of anyone living with dementia would like to obtain the Digital Talking Mats please fill in the attached Personal Digital Licence 161117 DTM personal licence form with explanation and send it to us at info@talkingmats.com
The Talking Mats digital app is available for organisations to purchase. This is an efficient way to support staff to evidence person centred planning.
The digital app typically operates via individual logons which means personal data is kept securely and it complies with data protection and client confidentiality. The individual with the logon can use their Digital Talking Mat with as many client/patients as they want.
We recognise that organisations may want to purchase several logons for staff to access digital Talking Mats and for that reason have created an Organisational Talking Mats digital licence. The savings are significant.
For application criteria please contact the Talking Mats office on 01786 479511
Why does Talking Mats work so well with children and adults with Down syndrome?
We have a great bit of video footage of Keir, a boy with Down’s syndrome, aged 9 years. He is using Talking Mats to talk about his life. Although Keir’s expressive speech is understood by his immediate family it can be harder for unfamiliar people to follow. Keir was able to communicate very clearly using his Talking Mat about what was going well and not so well. He used Makaton and key words to elaborate on some of his responses.Below is Keir’s Talking Mat. It looks like it would be good to do a submat on school.
We started to think about why Talking Mats can be such a great support for people with Down syndrome.
Here are our top ten reasons !
- In Down syndrome visuo-spatial processing is often viewed as a strength. Talking Mats uses a visual approach to communication.
- Receptive language skills are often better than expressive language skills. Talking Mat allows a thinker to express themselves visually talking the pressure off expressive speech.
- Vocabulary skills are often regarded as a strength and the Talking Mats framework relies on conceptual understanding.
- Talking Mats allows for extra processing time and space for the thinker to place the image on the mat. Reviewing the mat helps with auditory memory problems.
- The interviewer can then use the mat for conversation recasting (modelling a complete sentence) – so what you told me is……” You love going swimming because you like jumping in the water”
- Talking Mats allows you to explore topics that are of interest to the child or adult as well as topics that are functionally relevant.
- The Talking Mats images have words. A whole word approach can help literacy development. Symbols and words can also prompt speech production.
- Open questions are used which help to facilitate expression.
- Talking Mats can be used in lots of different settings: at home, in school and in the community.
- A Talking Mat conversation is FUN and supports relationship building and social closeness.
We know that every person with Down’s syndrome is a unique individual and we want to support them to further their communication, develop their interests, and become as independent as possible. Talking Mats is a great tool – why not give it a go. There’s lots more information on resources and training on www.talkingmats.com.
Self-management for people with long term conditions (LTC) is now a key government strategy to encourage people to take responsibility for their own health, behaviour and well-being. Talking Mats received funding from The Health and Social Care Alliance Scotland to look how using the Digital Talking Mats (DTM) can help people with LTCs to manage their health and well-being and to recognise their own strengths and abilities.
The overall aim of our project was to empower people with different long term conditions, to manage their own health and well-being. Through using Digital Talking Mats (DTM) we hoped that participants would be able to have more control over their lives and have improved communication with families and professionals.
There were a total of 28 participants in this project living with one of three different long term health conditions – stroke, dementia and learning disability. Each participant had access to a tablet device and was given a personal DTM licence which gave them access to 13 topics in the Talking Mats Health and Well-being resource. We visited each participant at home and taught them how to use it and asked them to complete and send us at least 1 digital mat per week for 6 weeks on any topic they wished. The design of the digital Talking Mat allowed them to email their mats directly to the researchers. We visited each participant a second time to discuss on how easy it was to use the digital Talking Mats and their views on their completed mats. We asked those who wished to, to continue sending us completed mats beyond the initial 6 weeks. We visited them again in 6 months to discuss how they were managing.
15 participants completed all 6 mats and 12 participants continued to complete mats over the length of the project. Participants completed 235 digital mats across all 13 topics
There were 3 particularly significant findings
1. At 18 months the participants living with dementia actually felt their well-being had improved, despite dementia being a progressive illness.
2. For the participants living with stroke the results were even more striking as 95% felt things were going well at the end of the project in comparison with 47% at the beginning.
3. At the end of the project the percentage of people with learning disability who felt things were not going well had reduced from 19% to 10%. Furthermore the percentage of people indicating that they were not sure about their views had increased from 27% to 42%. There can be a tendency for people with learning disability when using Talking Mats, to express their views at either end of the mat and to rarely use the mid- point. However being able to use the unsure mid- point is noteworthy as it indicates that the participants in the project realised that they could express their views not only as black or white but could indicate that they were unsure. This awareness opens up the potential for people to express views more thoughtfully with opportunities for further exploration.
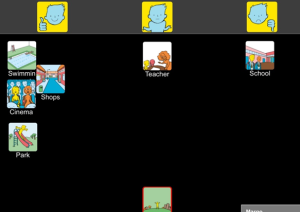
Here are three examples of how using the DTM supported people to self-manage situations in their lives. Click on image to enlarge.
As well as helping participants self-manage their long term conditions, an unexpected outcome of this project is that many people found that using the DTM helped them see the positive things in their life and not just the negative. It also highlighted that despite having a long term condition and, for many also a deteriorating one, that things were not getting worse.
Click here for full report including 6,12 and 18 month reports to the funders 20180717 Alliance full report
Click here for the summary report 20180717 Alliance Final Short Report
Click here for a video link of 2 participants
Moving from a primary school to secondary school can be a daunting prospect for children.
Whilst schools understand the need to prepare the children for the transition process, due to time constraints, the focus tends to be on group visits to the new school rather than one to one support for individual children.
The challenge therefore is to ensure that each child feels prepared for the transition and that they have the opportunity to talk about any worries they may have.
My sister is a head teacher of a small village school and was interested in finding out more about her pupil’s experience and thoughts about their impending move to secondary education.
With the permission of parents I offered a Talking Mats session to each child in the term prior to them leaving for secondary education. In total this was 8 children.
I used digital Talking Mats, choosing the “What I do and support” topic cards from the primary school pack.
The children were told that we were going to think about how each topic may be affected by moving up to secondary school. We used a happy/not happy top scale.
The level of engagement from the children first amazed me. They were all excited by the prospect of using the digital Talking Mat. All were familiar with iPad use and grasped the concept quickly.
They used the topic cards to think about areas such as playing, friends, helping in the house, looking after yourself, your safety and managing stress.
They all expressed worry about the transition process but for many it was not around areas that teachers or parents would have automatically considered. How they were going to get to and from the new school was a theme that concerned them, as well as getting up and getting ready to go to school in the morning. A large number of the children also explained that they had poor sleep due to either difficulty getting off to sleep or waking with worries. Some children also disclosed some concerns about family life.
I found that the diverse nature of the cards prompted the children to think about areas of their life that their teachers had not ordinarily thought about when considering the impact of transition.
As an occupational therapist it struck me that many of the children were expecting that with the change from primary to secondary there also came the added responsibility of having to look after themselves. For them the transition was not just about moving schools it was also about being more “grown up” and being less reliant on their parents for prompting their self care routine or accompanying them when outside.
At the end of the session a summary was agreed with each child and this was sent to both the teacher and the parent so that they could support the child with the issues they raised. The teachers remarked that even though each session had only lasted 20 minutes, and was facilitated by someone the child had never met before, it had managed to reveal a breadth of information about how each child was feeling, that they were not previously aware of.
In summary, the beauty of the Talking Mats approach is that it allows the thinker to explore a range of issues that are relevant to them and does not lead the listener down a path of asking questions they think to be relevant. This gave the child I worked with the opportunity to really say what was troubling them. They were not put off by the fact they have never met me before, they talked freely with the digital version of the Talking Mat being both a point of focus as well as in a format they enjoyed.
Whilst the theme of the sessions in this case was transition, I would commend teachers to consider using Talking Mats in schools to enable children of all ages to think and communicate their feelings on a wide range of topics.
Thanks again Rachel Woolcomb OT for a great practical example.
 Online training login
Online training login